
New transient mitral regurgitation, hypotension, diaphoresis, pulmonary edema or rales Known history of coronary artery disease, including myocardial infarction Reproduction of previous documented angina In the future, advanced diagnostic modalities, such as myocardial perfusion imaging, may have a role in reducing unnecessary hospitalizations.įindings indicating HIGH likelihood of ACSįindings indicating INTERMEDIATE likelihood of ACS in absence of high-likelihood findingsįindings indicating LOW likelihood of ACS in absence of high- or intermediate-likelihood findingsĬhest or left arm pain or discomfort as chief symptom

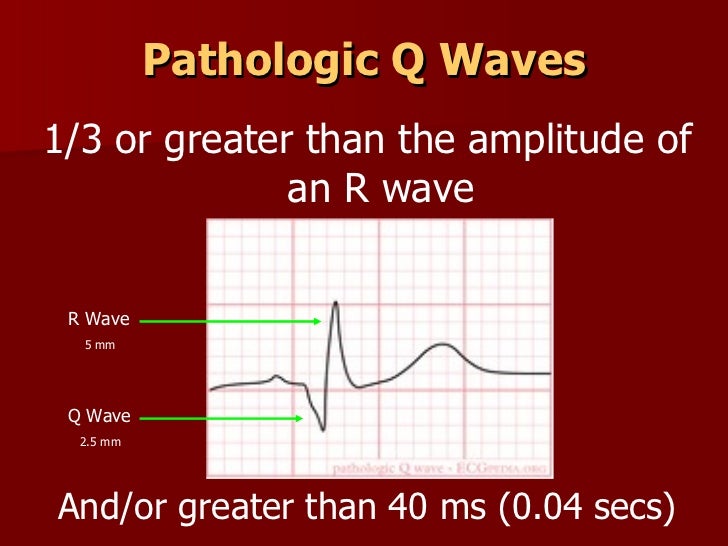
Early markers of acute ischemia include myoglobin and creatine kinase–MB subforms (or isoforms), when available. Troponin T or I generally is the most sensitive determinant of acute coronary syndrome, although the MB isoenzyme of creatine kinase also is used. Many low-risk patients can be discharged with appropriate follow-up. Intermediate-risk patients should undergo a structured evaluation, often in a chest pain unit. Most high-risk patients should be hospitalized. Risk stratification allows appropriate referral of patients to a chest pain center or emergency department, where cardiac enzyme levels can be assessed. In acute coronary syndrome, common electrocardiographic abnormalities include T-wave tenting or inversion, ST-segment elevation or depression (including J-point elevation in multiple leads), and pathologic Q waves. ECG Reference SITES and BOOKS the best of the rest. 100 ECG Quiz Self-assessment tool for examination practice. ECG Exigency and Cardiovascular Curveball ECG Clinical Cases. ECG A to Z by diagnosis ECG interpretation in clinical context. Diagnosis requires an electrocardiogram and a careful review for signs and symptoms of cardiac ischemia. ECG Library Basics Waves, Intervals, Segments and Clinical Interpretation. The term “acute coronary syndrome” encompasses a range of thrombotic coronary artery diseases, including unstable angina and both ST-segment elevation and non–ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. ECG Learning Center - Test Myocardial Infarctions Question 1: What can help to differentiate between the normal septal q wave and a pathologic Q wave A.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
